Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy
1. Instrument at MCPF
2. Windows materials
for UV/Vis
3. Solvent properties for
UV-Vis
MCPF is equipped
with Perkin Elmer Lambda 20 UV/VIS spectroscopy, the typical
specification as below:
| Optics |
Double beam
spectrometer with concave holographic grating with 1053 lines/mm |
| Sources |
Prealigned
deuterium and tungsten-halogen lamps with automatic source
change |
Wavelength
range
Transmission mode
Diffusion Reflection Mode |
190-1100 nm
250-1100 nm |
| Stray
radiation |
0.01 %T at
220, 340, 370 nm |
| Wavelength
accuracy |
±0.1 nm at D2
peak 656.1 nm |
| Wavelength
repeatability |
±0.05 nm at D2
peak 656.1 nm |
| Bandpass |
<1 nm or
<2 nm fixed |
| Photometric
accuracy |
±0.003A at
1A, measured with NIST 930 filters |
| Photometric repeatability |
±0.001 A at
1A |
| Stability |
0.00015A/h (at
500 nm, 2s response) |
| Baseline
flatness |
0.0005 A, 2 nm
slit
0.001 A, 1nm slit
(200-1100 nm at 0A,
smooth 2, 240 nm/min) |
| Noise level |
0.00003 A (0A,
500 nm, 2 s response), RMS |
2.
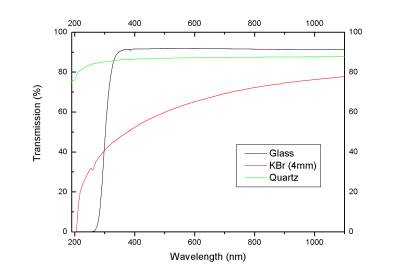
Window Materials
for UV-VIS measurement
3. Solvent
Properties for UV-Vis
The solvent should meet the following
requirements:
·
It should dissolve the sample without reacting with it.
·
The radiation absorption in the scanning region should be low. High
absorption by the blank reduces the reference energy, thus increasing
noise.
·
Evaporation should be fairly low at ambient temperature.
In general, aromatic compounds exhibit high
absorption in the UV region and hence are not suitable as solvents for
measurements in this region.
Water is virtually the only useful solvent
below 195 nm, but it must be freed from oxygen to attain best
transmission.
Whenever you are going to use a solvent with
unknown absorption characteristics, scan its spectrum first to
determine whether it is suitable.
The lower wavelength limits of a number of
commonly used solvents are presented in the following table. The lower
limit has been defined as that wavelength at which 10 mm of pure solvent
has a transmission of 10
%.
Lower Wavelength Limits of Solvent for UV-Vis
Measurement
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acetone |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Tetrachloroethylene |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
m-Xylene |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Toluene |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Benzene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
N,N-Dimethylformamide |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Ethyl Propionate |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Carbon Tetrachloride |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Ethyl Formate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Butyl Acetate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Methyl Formate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Ethyl Acetate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Chloroform |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
1,2-Dichloroethane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dichloromethane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Glycerol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Dioxan |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Hexane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
i-Octane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trimethylpentane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acetonitrile |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cyclohexane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Methanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
i-Propanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Methylcyclohexane |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Water |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
190(nm) |
210 |
230 |
250 |
270 |
290 |
310 |
330 |
350 |
370(nm) |
Last
updated on
18/12/2005
|
