|
|
Fourier
Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation
3. Infrared Window Materials
4. Characteristic IR Band
Position
5. IR Unit Conversions
6. Instrument at MCPF
t>
1. Introduction
What information can IR spectroscopy provide?
-
Molecular vibrate with frequency
in IR range
-
Identify unknown chemicals by
matching spectra with known database
-
Structural ideas: can determine
chemical groups in a specific compound
-
Optical or electronic properties
in IR range
What does FT-IR measure?
AMolecule may absorb infrared radiation of the
appropriate frequency to excite it from one vibrational or
rotational level to another.
FT-IR measures the absorption spectra which
characterize the particular molecular and its molecular motions
nSolid samples
pPowders: You can press powder into a pellet. In this
method, you can select different diluents (matrixes) for various
applications. For mid-IR frequency range, KBr, KCl
can be used. For far-infrared testing, high-density
polyethylene (HDPE). For near-infrared analysis, CsI or KBr can be
selected.
qSmall size or nonuniform : IR Microscopy
qThin Film: Direct transmission or Attenuated Total
Reflection (ATR)
qThin Film on Substrate: Specular or diffuse
reflection
nLiquid samples
qDrop of liquid on salt disc (no water)
qLiquid cell
qATR
For all non-self-supported samples, an IR
transparent substrate or container (IR window) is required for
transmission measurement. The selection of window materials is based on your
interested wavenumber range and the properties of the materials. The followed
table can help you to chose the window material for your experiment. MCPF only
can provide with limited NaCl and KBr powder for your sample preparation.
Window Selection Guide
| Material |
Range
(cm-1) |
Refractive
Index
(at 2 Ám) |
Mid-IR
%T Graph |
Properties |
| AgBr |
22,000-286 |
2.30 |
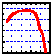 |
A soft crystal; insoluble in
water; darkens upon exposure to UV radiation; will cold flow. |
| AgCl |
10,000-360 |
2.07 |
 |
Soft crystal that is insoluble
in water; darkens upon exposure to UV radiation; will cold flow. |
| Al2O3
(Sapphire) |
50,000-1,650 |
1.5 |
|
Glass-like |
AMTIR
(GeAsSe Glass) |
11,000-625 |
2.5 |
|
AMTIR (Amorphous Material
Transmitting IR) is a glass; insoluble in water, resistant to corrosion. |
| BaF2 |
67,000-740 |
1.46 |
 |
A hard, brittle crystal;
insoluble in water; good resistance to fluorine and fluorides; no fog. |
| CaF2 |
77,000-1,110 |
1.42 |
 |
A strong crystal; resists most
acids and alkalis; withstands high pressure; insoluble in water; no fog. |
| CdTe |
20,000-400 |
2.67 |
|
Lower thermal conductity than
ZnSe (used with CO2 lasers). Attacked by oxidizers. Also
known as Irtran-6. |
Chalcogenide
(AsSeTe glass) |
4,000-900 |
2.8 |
|
Good for Mid-IR fiber optics;
chemically inert. |
| CsI |
40,000-200 |
1.74 |
|
Soft crystal; soluble in water;
hydroscopic; offers an extended transmission range. |
| Diamond |
25,000-33 |
2.37 |
|
Phonon bands around 1900-2600,
except in Type IIa diamonds. Very useful for high-pressure or corrosive
work. |
| GaAs |
7,000-650 |
3.33 |
|
Hard crystal, can be made
amorphous |
| Ge |
5,500-600 |
4.00 |
 |
A hard, brittle crystal;
insoluble in water; well suited for ATR. |
Irtran-1 (see MgF2)
Irtran-2 (see ZnS)
Irtran-3 (see CaF2)
Irtran-4 (see ZnSe)
Irtran-5 (see MgO)
Irtran-6 (see CdTe) |
(Irtran is a
registered trademark of the Eastman Kodak Company) |
| KBr |
40,000-400 |
1.53 |
 |
Very soft, water soluble
crystal; low cost and good transmission range; fogs. |
KRS-5
(Thallium Bromide-Iodide) |
20,000-250 |
2.37 |
 |
A soft crystal, deforms under
pressure; good ATR material. Soluble in bases and insoluble in acids.
Toxic. |
| LiF |
95,000-1,700 |
1.4 |
|
Best VUV transmitter available |
| MgF2 |
87,000-1,250 |
1.35 |
 |
|
| NaCl |
40,000-625 |
1.52 |
 |
Very soft, water soluble
crystal; low cost and good transmission range; fogs. |
Polyethylene
(high density) |
600-30 |
1.54 |
|
Excellent for Far-IR, very
cheap, attacked by few solvents, difficult to clean |
| Pyrex |
30,000-4,000 |
1.473 |
 |
Labware glass |
| Si |
83,300-660 300-0
(depends on doping) |
3.40 |
 |
A hard and brittle crystal;
inert; ideal material for far-IR. |
| SiO2 (Quartz) |
65,000-2,700 |
1.4 |
 |
A hard crystal, clear in the
visible |
ZnS
(Cleartran) |
17,000-833 |
2.2 |
 |
A water-free form of ZnS.
Insoluble in water. Also known as Irtran-2 |
| ZnSe |
17,000-720 |
2.2 |
 |
A hard and brittle crystal;
inert; ideal material for ATR. Also known as Irtran-1. |
The followed table list some common
characteristic IR band in polymers. MCPF suggests the users to do reference
search before submitting your samples for IR analysis.
| Group |
Frequency Range (cm-1) |
| OH stretching vibrations |
|
| Free OH |
3610-3645 (sharp) |
| Intramolecular H bonds |
3450-3600 (sharp) |
| Intermolecular H Bonds |
3200-3550 (broad) |
| Chelate Compounds |
2500-3200 (very broad) |
| NH Stretching vibrations |
|
| Free NH |
3300-3500 |
| H bonded NH |
3070-3350 |
| CH Stretching vibrations |
|
| =-C-H |
3280-3340 |
| =C-H |
3000-3100 |
| C-CH3 |
2862-2882, 2652-2972 |
| O-CH3 |
2815-2832 |
| N-CH3 (aromatic) |
2810-2820 |
| N-CH3 (aliphatic) |
2780-2805 |
| CH2 |
2843-2863,2916-2936 |
| CH |
2880-2900 |
| SH Stretching Vibrations |
|
| Free SH |
2550-2600 |
| C=-N Stretching Vibrations |
|
| Non-conjugated |
2240-2260 |
| Conjugated |
2215-2240 |
| C=-C Stretching Vibrations |
|
| C=-CH (terminal) |
2100-2140 |
| C-C=-C-C |
2190-2260 |
| C-C=-C-C=-CH |
2040-2200 |
| C=O Stretching Vibrations |
|
| Nonconjugated |
1700-1900 |
| Conjugated |
1590-1750 |
| Amides |
~1650 |
| C=C Stretching Vibrations |
|
| Non-conjugated |
1620-1680 |
| Conjugated |
1585-1625 |
| CH Bending Vibrations |
|
| CH2 |
1405-1465 |
| CH3 |
1355-1395, 1430-1470 |
| C-O-C Vibrations in Esters |
|
| Formates |
~1175 |
| Acetates |
~1240, 1010-1040 |
| Benzoates |
~1275 |
| C-OH Stretching Vibrations |
|
| Secondary Cyclic Alcohols |
990-1060 |
| CH out-of-plane bending vibrations
in substituted ethylenic systems
|
|
| -CH=CH2 |
905-915, 985-995 |
| -CH=CH-(cis) |
650-750 |
| -CH=CH-(trans) |
960-970 |
| C=CH2 |
885-895 |
| |
|
Here is some constants for unit conversion
for FT-IR data processing:
Energy unit conversions:
| 1 cm-1 = |
|
0.124 meV |
0.030 THz |
1.44 Kelvin |
| 1 meV = |
8.1 cm-1 |
|
0.242 THz |
11.6 Kelvin |
| 1 THz = |
33 cm-1 |
4.14 meV |
|
48 Kelvin |
| 1 Kelvin = |
0.70 cm-1 |
0.086 meV |
0.021 THz |
|
Conversions for microns (wavelength) to and from wavenumbers (cm-1):
| microns = 104 / x cm-1 |
| cm-1 = 104 / x microns |
Absorbance units:
A = log ( 1/T )
Where A is Absorbance and T is Transmittance |
The optical lab of MCPF is equipped with a FT-IR reserach
system: Bio Rad FTS 6000. The
FTS 6000 Spectrometer is a high performance research grade multi-range FT-IR
spectrometer capable of both rapid scan and step scan operation and covering the
spectral range 50,000-10 cm-1. Its high quality 60o
Michelson air bearing piezoscan interferometer features piezoelectric-based
continuous dynamic alignment and an interchangeable beamsplitter design. Other
features include operation into the UV/Visible range and patented in-scan
co-adding (providing effective 22 bit A/D operation). The piezoscan
interferometer is capable of spectral resolution to 0.10 cm-1.
6.1
Specification
Note: The typical setting of FTIR is :
Transmission: Mid IR 400-4000cm-1, 4 cm-1 resolution.
ATR ZnSe Crystal: Mid IR 650-4000cm-1, 4 cm-1 resolution.
Microscopy: Mid IR 700-4000cm-1, 4 cm-1 resolution.
| Spectrometer optical bench |
|
| Interferometer |
Stable air-bearing type 60 degree
Michelson interferometer
Automatic beamsplitter alignment
Real time dynamic alignment during scan with three piezoelectric
actuators at the back of the fixed mirror. |
| Source |
Mid-IR: High intensity water cooled
ceramic source
Far-IR: Mercury arc lamp
Near IR: Tungsten halogen lamp
UV-Vis: Xenon lamp |
| Beamsplitter |
Mid-IR: Germanium on KBr beamsplitter
Far-IR: A set of 5 Mylar beamsplitter
Near IR: Quartz beamsplitter.
UV-Vis: UV Quartz beamsplitter |
| Range |
Mid-IR: 6000-400 cm-1
Far IR: 600-10 cm-1
Near IR: 15800-3000 cm-1
UV-Vis: 30,000-15800 cm -1 |
| Detector |
Mid-IR: DTGS with CsI window
Far-IR: DTGS with PE window in dual detector plate
Near IR: PdSe detector & Si detector in dual detector plate
UV-Vis: UV detector assembly with R166, R466 & IP28 PMT detctors |
| Resolution |
Better than 0.1cm-1 (FWHM=0.08
cm-1) |
| Rapid-Scan |
Better than 80 scans/second at 32 cm-1 resolution |
| Step-Sacn |
Step rate from less than 1 Hz to 800
Hz (in Far, Mid & Near IR) |
| TRS |
Time-resolved spectroscopy, with time
resolution of 5 Ás |
| Phase modulation: |
Phase and amplitude modulation |
| Microscope |
|
| Operation mode |
Transmission, Reflection & Side
Reflection |
| Objective |
15X Schwartzchild objective |
| Condenser |
Two 15X Schwartzchild condensers. |
| Eyepieces |
10X eyepiece. |
| Viewer |
Trinocular viewer |
| Sampling area |
Less than 10x10 Ám up to 250x250 Ám
(Transmission & Reflection) |
| Stage |
2"X3" manual stage |
| Polarzier |
IR Polarizer |
|
|
Last updated on 07/08/2017
|

